A small aneurysm or one that doesn't cause actionable symptoms may not require surgical treatment until it reaches a certain size or is growing in size over a short period. Your doctor may recommend "Watchful Waiting."
Watchful Waiting shall include an ultrasound, CT scan or other relevant test every 6 months to closely monitor the aneurysm, and medication to treat the underlying condition like blood pressure or cholesterol levels.
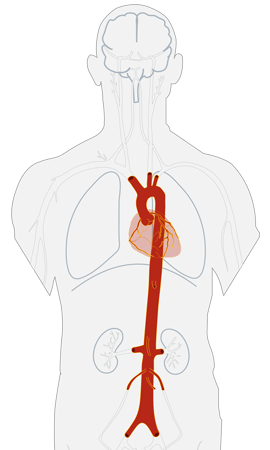
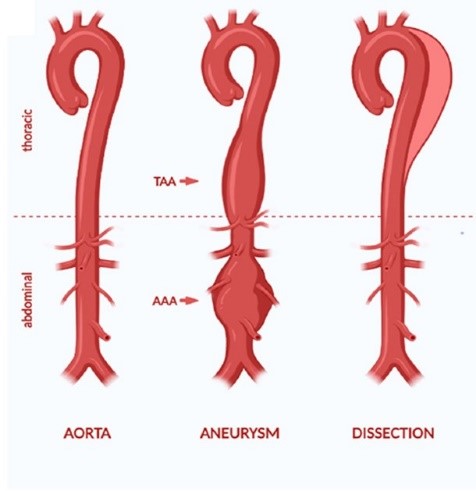
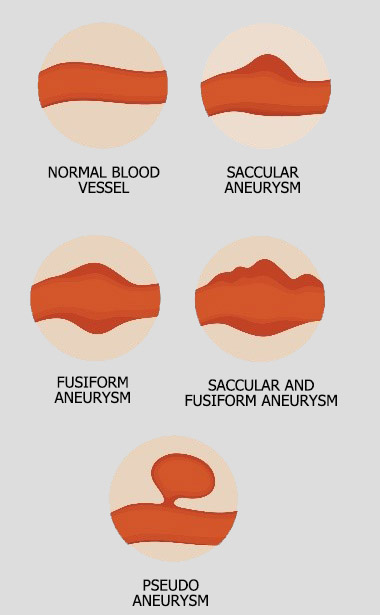
As explained earlier, Aorta is a thick & flexible artery with its diameter varying as it descends to the lower abdomen. Though not a standard medical practice but a general guidance, bulging which is more than 1.5 times of the normal diameter in the section is considered a stage which requires medical interventions.
When the aneurysm has reached a size, as per assessment by a specialist, benefits of repairing the aneurysm outweigh the risks associated with interventional procedures, doctor shall provide you with treatment options as mentioned below. It should be noted that basis the location, size of aneurysm and the overall medical condition of the patient, some of the options may not be available for a given patient.
Aortic Aneurysm Open Surgical Repair: An incision is made to directly visualize and repair the aneurysm. A cylinder-shaped tube which is called a graft may be used to repair the aneurysm. This is sewn to the artery, connecting the two ends of the artery at the site of the aneurysm. The open repair is considered the surgical standard for an aortic aneurysm repair. Grafts are made of various materials, such as Dacron (textile polyester synthetic graft) or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, nontextile synthetic graft).
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). EVAR is a procedure that requires only small incisions in the groin along with the use of X-ray guidance and specially designed instruments to repair the aneurysm. With the use of special endovascular instruments and X-ray images for guidance, a stent-graft is inserted via the femoral artery and advanced up into the aorta to the site of the aneurysm. A stent-graft is a long cylinder-like tube made of thin metal mesh framework (stent), while the graft is made of various materials, such as Dacron or PTFE. The graft material may cover the stent. The stent helps to hold the graft open &in place thus reducing pressure on the blood vessel and prevents rupture.
EVAR is technologically advanced and more preferred modern line of treatment. However location of the bulge, health condition of the patient governs the choice of treatment plan & hence discuss the treatment options available with you with specialist doctors like interventional radiologist who are endovascular specialist.